The power of collaboration: How shelter companies, clusters and industrial parks stimulate nearshoring in supply chain management in Mexico
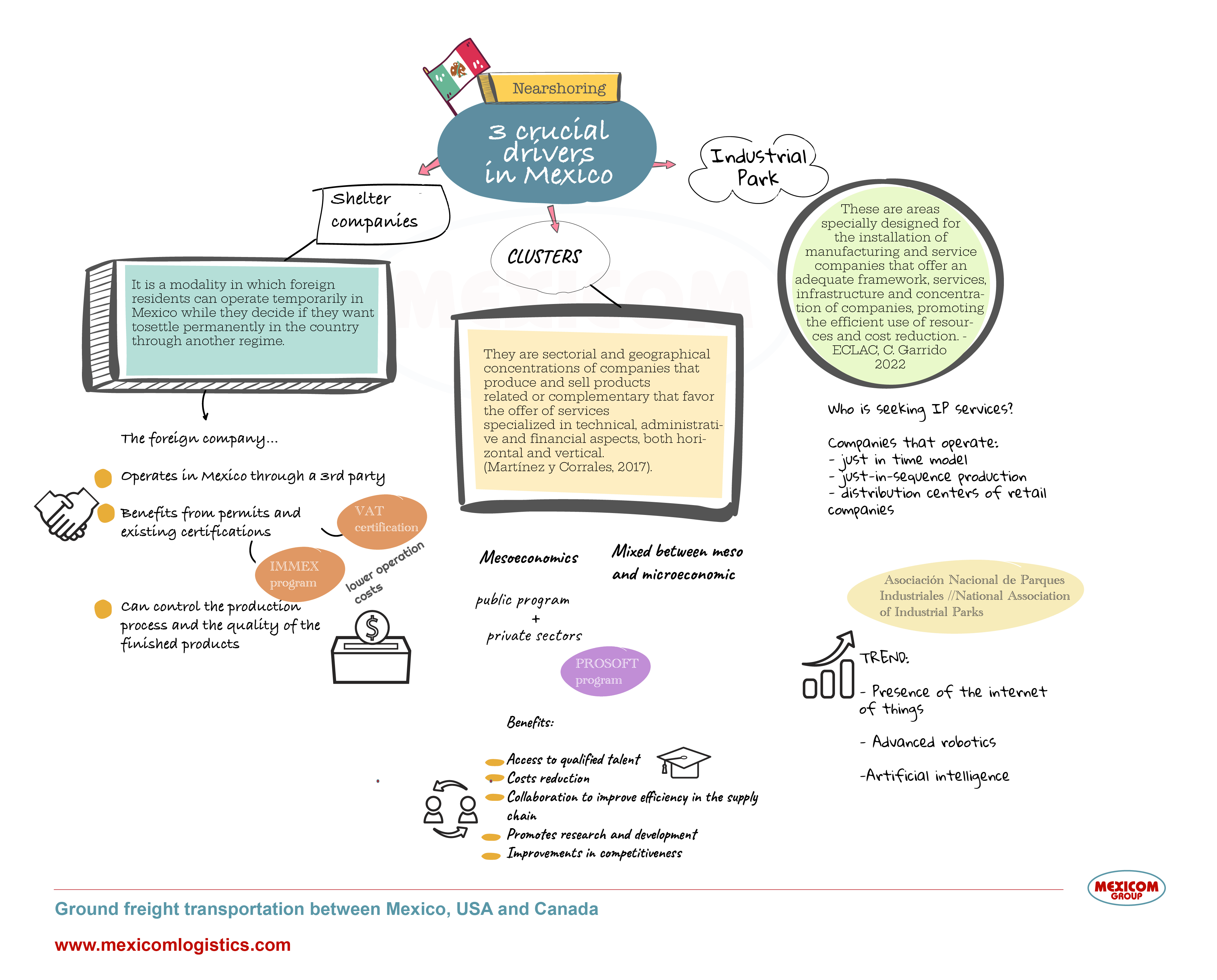
To promote Nearshoring in Mexico, shelter companies, clusters, and industrial parks have played a crucial role. These organizational developments work collaboratively to create a conducive environment for investment, offering high-quality services and promoting innovation and competitiveness. In his work published by ECLAC, Celso Garrido takes us by the hand to understand the role of these organizational developments that have stimulated and made nearshoring possible in Mexico.
Benefits of the shelter maquiladora regime in Mexico for foreign companies
What is a shelter maquiladora company?
The shelter maquiladora regime is a way in which foreign residents can operate temporarily in Mexico while they decide if they want to settle permanently in the country through another regime.
The companies of foreign residents that operate through a shelter maquiladora company can remain in this regime for up to a maximum of four years or fiscal years from the beginning of their operations in Mexico.
During this period, they can recoup their investments and expand their services, and they also have the option of establishing a permanent place of business in the country and paying taxes once the transition period has ended.
The benefits of shelter companies in Mexico:
First, the foreign company can have operations in Mexico through a third party, which means that the shelter company absorbs all the risks and liabilities of the Mexican entity.
Second, by using the services of a shelter company in Mexico, the foreign company benefits from already existing permits and certifications, such as the IMMEX program and VAT certification, which significantly reduces the annual cost of operation.
“The Program for the Manufacturing, Maquiladora and Export Services Industry (IMMEX) allows you to obtain a program to carry out temporary imports of merchandise with production processes and/or services to export merchandise or to provide export services, deferring the payment of the general import tax, Value Added Tax and, where applicable, compensatory quotas for the goods necessary to be used in an industrial or service process for the production, transformation or repair of goods of foreign origin imported temporarily for their export or the provision of export services.”
More information about the IMMEX Program for industrial, service and lodging companies, here
Third, the foreign company can control the production process and the quality of finished products more efficiently and competitively than if they outsourced or contracted manufacturing.
This business modality is subject to transformations due to changes in the regulatory and tax frameworks that are currently underway, but according to analysts this would mean an improvement in the operations of these entities.
Industrial clusters as the core point of nearshoring: drivers of business development and channel for the circulation of knowledge in Mexico
Clusters in Mexico promote nearshoring by fostering inter-company cooperation, innovation, and the development of technology and human capital in specific regions. This in turn improves the competitiveness of companies and economies in general.
In Mexico there is a diverse set of clusters identified with industries and states, such as the automotive, electronics, textile, aerospace, aeronautical, medical device, and biotechnology clusters, among others.
“Clusters are sectoral and geographical concentrations of companies that produce and sell related or complementary products that favor the offer of specialized services in technical, administrative and financial aspects, both horizontal and vertical. (Martinez and Corrales, 2017).“
There are two levels of concretion of the clusters in Mexico: At the mesoeconomic level, with the promotion of a public program in alliance with business sectors to promote innovation, as in the case of the Software Industry Development Program and Innovation (PROSOFT).
Secondly, at a mixed level between meso and microeconomic and also mixed in its institutional nature, since some result from interactions between business and public initiatives and others are mainly private.
These clusters favor inter-business cooperation, the formation of links, supply, subcontracting, chains, among others, at the business and sector level. In addition, the concentration of companies in a specific territory generates externalities of technological development and human capital that contribute to the performance of economies.
Benefits of industrial clusters:
- Access to qualified talent: Clusters are groups of companies that operate in the same industry and are geographically located close to each other. Being in a cluster, companies can access a pool of qualified talent in the geographical area, which facilitates the hiring of trained personnel and reduces training costs.
- Cost reduction: The geographical proximity of the companies that operate in a cluster allows sharing resources and knowledge, which reduces production costs. In addition, clusters may have access to tax incentives and government programs designed to promote industry growth.
- Increased Supply Chain Efficiency: By being geographically located close to each other, companies can work collaboratively to improve supply chain efficiencies. This can include the consolidation of purchases and shipments, as well as the sharing of information and resources.
- Ease of research and development: Clusters usually have a concentration of research centers and universities specialized in the industry in question. This allows companies to access research and development in the field and establish collaborations for innovation projects.
- Improvements in competitiveness: By being located close to each other, companies can learn from best practices and compete with each other to improve their efficiency and productivity. This can generate an improvement in the competitiveness of the industry in general and attract more companies to the region.
Automotive Cluster in Mexico
In general, these clusters usually have a major assembly company in the industry in
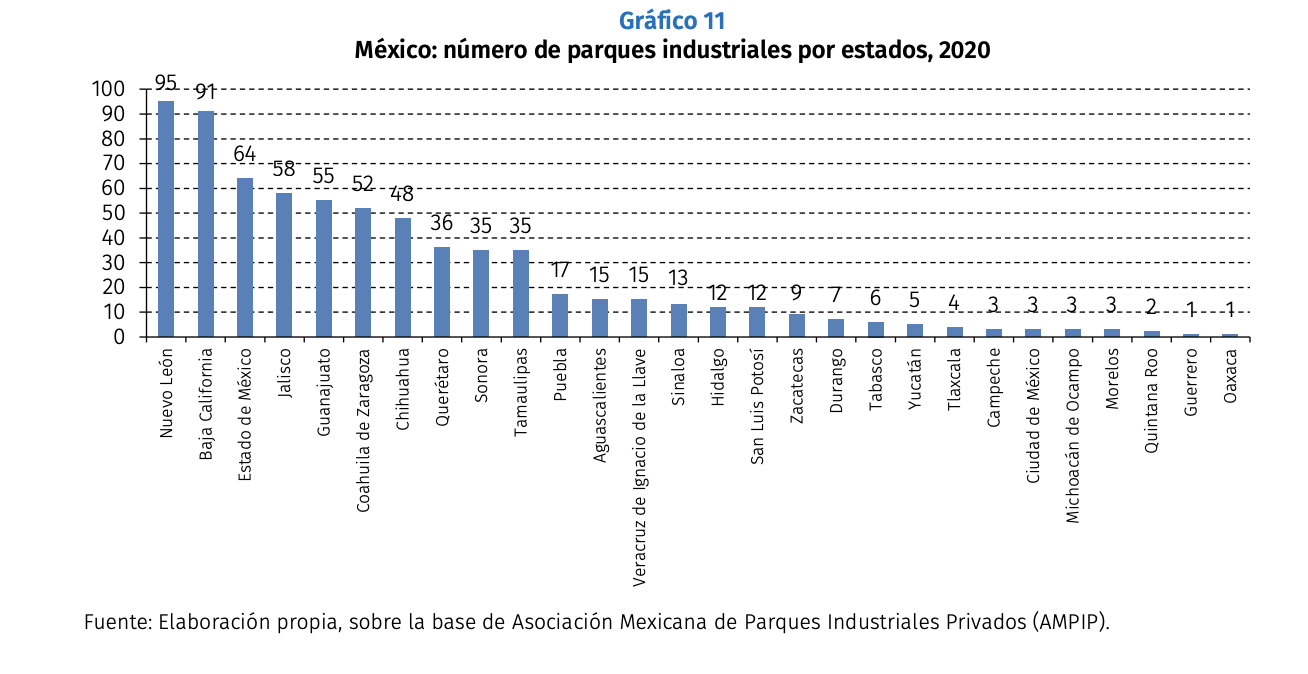
around which companies of various kinds are articulated. Clusters are very useful for the development of companies that operate in the respective industry due to the effects of cooperation between companies that take place in them. An outstanding case is the automotive industry cluster, from which independent entities have developed in ten states, such as Nuevo León, San Luis Potosí, Guanajuato, the State of Mexico, Chihuahua, Aguascalientes, Querétaro, and Jalisco.
Based on this evolution, the National Network of Automotive Industry Clusters has been configured, which operates as a leader for the development of the industry.
REDCAM promotes the integration of SMEs and national inputs into production chains, in line with the new perspectives proposed by the T-MEC. REDCAM also establishes cooperation agreements with equivalent agencies in the United States and Europe. In this sense, REDCAM is relevant not only for the development of the industry, but also for attracting nearshoring investments and for promoting the circulation of knowledge among the members of the cluster and their international counterparts.
“This combination of strategic dynamics with operational issues also seems to occur in other clusters, with which they become not only drivers of the chains and the regions in which they participate, but also powerful channels for the circulation of knowledge among the members. of the cluster, but also because of its relations with international counterparts…
Likewise, this configuration and development of clusters has also been a relevant factor in promoting and consolidating new industries related to CPGs in the country, such as the aerospace industry, which is a frontier sector worldwide, or medical devices whose cluster is the leader in Latin America.” Celso Garrido – ECLAC
Industrial parks
Industrial parks are areas specially designed for the installation of manufacturing and service companies that offer an adequate framework, services, infrastructure and concentration of companies, promoting the efficient use of resources and cost reduction. They have become one of the most efficient and effective instruments to stimulate innovation and growth in Mexico and attract foreign direct investment.
In Mexico, industrial parks date back to the 1960s, related to the implementation of the maquiladora program, and were initially located in the border states, serving US companies. Most of the companies with industrial parks are located in states close to the US border and most are focused on the automotive industry.
Since then, the business model has evolved, offering not only lots for companies to set up, but also buildings for rent, new infrastructures and digital services related to industry 4.0. Given its complexity, the business of Industrial Parks in Mexico is mainly operated by private real estate investment entities such as investment funds or real estate investment consortiums such as Real Estate Investment Trusts (FIBRAS).
The companies that seek IP services in the country are mainly those that operate in just-in-time models, in just-in-sequence production models, or those that have distribution centers of retail companies, such as warehouses for logistics operators.
The National Association of Industrial Parks (ANPIP) has carried out a prospective analysis exercise for Industrial Parks which shows a growing trend towards the presence of the Internet of Things, advanced robotics and artificial intelligence.
For example, industrial parks in Mexico’s border states, such as Baja California and Chihuahua, have attracted US companies looking to move their production from China to Mexico due to geographic proximity and lower labor costs.Likewise, the development of high-quality IP with digital services related to Industry 4.0 and shelter company services, such as those in Ciudad Juárez, has attracted investment from companies such as Foxconn, which is building a plant in this city to produce screens. LCD for televisions and other electronic products.
In general, Industrial Parks in Mexico have evolved to offer a wide range of services and personalized solutions to the needs of companies, which makes them an effective instrument to attract foreign direct investment and encourage nearshoring.
Sources:
Martínez, G. y S. Corrales (2017), “Cadenas productivas y clusters en la economía regional de Nuevo León: un análisis de matriz insumo-producto”, Revista Economía Teoría y Pr.
Garrido, México en la fábrica de América del Norte y el nearshoring (LC/MEX/TS.2022/15/-*), Ciudad de México, Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe (CEPAL), 2022










Wonderful blog!