Key changes in Globalization 4.0
Globalization 4.0 is one of the top topics on the international agenda and will be the theme of the next annual meeting of the World Economic Forum – 22-25 January 2019-. Globalization 4.0, which emerged in the midst of the fourth industrial revolution, is a new phase of international cooperation, in which sectors such as health, transportation, communication, production, and distribution, to name a few, will be drastically affected by the new technological wave.
The evolution of globalization in brief
Gobalización 1.0, in the times of Columbus, was characterized by the exploration of the world and the “discovery” of new geographies. The steam engine reduced the cost of consuming goods from a distance. International arbitration was little or not existent.
Globalization 2.0 The multinationals start doing business abroad. These are the times of the early days of the Internet. Institutions for international governance are created, such as the United Nations. the IMF and the World Bank.
The Globalization 3.0 The companies of the most advanced economies of the world moved the labor and the know-how to economies where wages are lower, achieving greater efficiency and lower production costs. Workers in the manufacturing sector were affected by this change.
What is Globalization 4.0 about?
During Globalization 4. 0, the impact of Globalization 3.0 is extrapolated to the services and the technology sectors. The economy is increasingly driven by data, which transforms global value chains and drives participation from different geographic locations and regions.
Digital technology changing the wage arbitrage in the service sector
The technological advances of globalization 4.0 allow people to work, direct business, and access databases from anywhere in the world. Richard Baldwin, Professor of International Economics in Geneva calls this phenomenon “telemigration”, when people can sit in a geographical region to work in an office located in another part of the globe. “The geographical separation of labor and labor services through digitech that makes remote workers seem less remote.” While in globalization 3.0 workers in the manufacturing sector suffered the most, in Globalization 4.0 “digital technology – or digitech, for short – is tearing down the barriers to wage arbitrage in the service sector. ”

Expansion opportunities for small businesses
E-commerce opens the doors for small businesses to sell their products to a market that is scattered around the world. Technological advances and interconnectivity allow us to break with the belief that only large companies make exports and distribute their services in different countries. In the United States, 67% of exporters have less than 20 employees.
Read also: Understanding the USA-Mexico shipping process
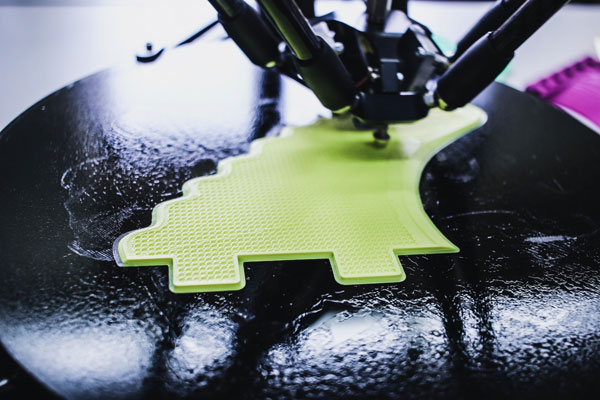
New industrial technologies to create value
“New industrial technologies – including 3D printing, new forms of factory automation and machine learning – are rapidly enabling the mass personalization of products and local optimization of supply and demand. As a result, the maker movement and the sharing economy are both expanding rapidly. This is increasing the number of people who can use technology to create value”, explain Nicholas Davis and Derek O’Halloran, members of the executive committee of the World Economic Forum.
Institutional redesign and the opportunity to reinforce positive values
Globalization 4.0 has only just begun, but we are already vastly underprepared for it. Clinging to an outdated mindset and tinkering with our existing processes and institutions will not do. Rather, we need to redesign them from the ground up, so that we can capitalize on the new opportunities that await us, while avoiding the kind of disruptions that we are witnessing today. Says Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum
Technological changes intricately involve social and economic changes. Globalization 3.0 brought consequences in the disparity of wealth and inequality, now globalization 4.0 is a new opportunity for changes to be made with regulatory frameworks focused on positive, inclusive, reliable and sustainable values.
“What does this mean? Well, at the same time as we celebrate the opportunities of AI to make our organizations more productive, we need to be closing the digital divide and making sure algorithms challenge, rather than reinforce, existing prejudices and discrimination. And, as we start to use distributed ledgers to revolutionize global finance, we need to be deploying the blockchain to help refugees prove their identity and to help civil society organizations track commitments to sustainability.” Señalan Davis y O’Halloran.
Related articles: Blockchain and its impact in the supply chain

Globalization 4.0 presupposes a challenge that tests our capacity for adaptation and resilience, as the previous phases of globalization have done. It also implies a new opportunity to readjust ad create rules that place the preservation of human dignity as the main interest.
Sources:
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/12/if-this-is-globalization-4-0-what-were-the-other-three/
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/11/the-fourth-industrial-revolution-is-driving-a-new-phase-of-globalization/
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/11/globalization-4-what-does-it-mean-how-it-will-benefit-everyone/
http://www.europeanbusinessreview.eu/page.asp?pid=2823
ciedec.org/resources/exporting-facts/
Other articles:
Cálculo de los tiempos de tránsito para cargas que viajan desde Canadá y Estados Unidos hacia México
4 sitios web imprescindibles con indicadores económicos a nivel global
Menos de 10% de las empresas manufactureras utiliza “IoT” (Internet de las Cosas)











I really enjoyed this content, it is amazing information for the readers. I hope to see more in future.